In the dynamic world of logistics, the integration of Information Technology (IT) has been a game-changer. While the advantages of IT in logistics are numerous, like any technological implementation, it also comes with its own set of challenges. This article aims to explore both sides of the coin, providing a comprehensive understanding of how IT influences the logistics sector.
Advantages of IT in Logistics
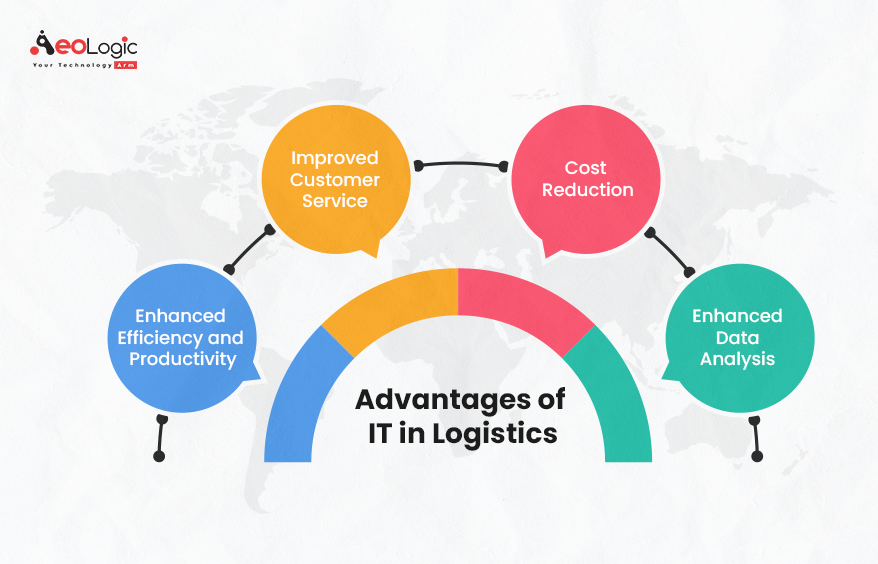
In the fast-paced realm of logistics, the infusion of Information Technology (IT) stands as a beacon of progress and efficiency. Let’s delve into the numerous advantages of IT in logistics, exploring how it reshapes the landscape of this critical industry.
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most significant advantages of IT in logistics is the dramatic increase in efficiency and productivity. Automation of processes, from inventory management to order processing, reduces human error and speeds up operations. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, companies that digitize their supply chains can expect to boost annual growth of earnings before interest and taxes by 3.2% and annual revenue growth by 2.3%.
- Real-Time Tracking: Advanced tracking systems allow for real-time updates on shipments, enhancing transparency and enabling better decision-making.
- Automated Inventory Management: IT systems can predict inventory needs, manage stock levels, and reduce the costs associated with overstocking or stockouts.
Improved Customer Service
IT enables logistics companies to provide better customer service. With tools like real-time tracking and automated notifications, customers stay informed about their shipments, leading to increased satisfaction.
- Personalized Experiences: IT systems enable logistics companies to offer personalized service options, such as preferred delivery times and real-time updates, enhancing the overall customer experience.
- Faster Problem Resolution: With IT tools, customer service teams have immediate access to shipment data, enabling quicker and more effective resolution of any issues or queries.
- Enhanced Communication: IT facilitates better communication channels between logistics providers and customers, ensuring that customers are always informed and engaged throughout the delivery process.
Also read: Top IT Consulting Companies in the World 2023
Cost Reduction
Technology helps in identifying inefficiencies and cutting costs. For instance, route optimization software can reduce fuel consumption and vehicle maintenance costs.
- Optimized Warehouse Operations: IT solutions enable smarter warehouse management, reducing waste and lowering storage costs by efficiently organizing inventory and streamlining picking and packing processes.
- Decreased Paperwork and Administrative Costs: By digitizing records and automating administrative tasks, IT in logistics significantly cuts down on paperwork, leading to reduced labor and material costs.
- Scalable Solutions for Variable Demand: Advanced IT systems provide the agility to scale operations up or down based on demand, ensuring that resources are not wasted during slower periods and are adequately allocated during peak times.
Enhanced Data Analysis and Decision Making
The use of Big Data and analytics in logistics helps in making informed decisions. This leads to optimized operations and better resource allocation.
- Predictive Analytics for Proactive Solutions: IT enables logistics companies to use predictive analytics, which helps in foreseeing potential disruptions and planning accordingly. This proactive approach minimizes risks and enhances overall operational resilience.
- Customer Insights for Tailored Services: By analyzing data trends, logistics firms can understand customer preferences and behavior better, allowing them to tailor their services for improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: IT systems facilitate more accurate forecasting of demand, which aids in the efficient allocation of resources like vehicles, personnel, and warehouse space, ensuring optimal utilization and reducing wastage.
Also read: The Role of IT Consulting in Business Growth and Strategy
Disadvantages of IT in Logistics

While the integration of Information Technology (IT) in logistics has brought significant improvements, it’s important to understand the challenges and drawbacks associated with its use. The disadvantages of IT in logistics are multifaceted and can impact businesses in various ways.
High Initial Investment Costs
The implementation of IT systems in logistics is often associated with high initial costs. This financial burden can be a significant barrier, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. The cost includes not just the immediate expenses of purchasing software and hardware, but also the long-term investment in maintaining and updating these systems.
- Capital Intensive: Implementing IT solutions in logistics often requires a substantial initial investment. This includes the cost of purchasing software, hardware, and other necessary technologies. For smaller businesses, these costs can be prohibitively expensive, hindering their ability to compete with larger companies that have more financial resources.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Beyond the initial setup, maintaining IT systems can be costly. Regular software updates, hardware upgrades, and IT support services add to ongoing expenses.
Cybersecurity Risks
As logistics operations increasingly depend on digital solutions, the risk of cybersecurity threats grows. These risks encompass a range of issues from data breaches to operational disruptions. Companies must invest in robust security measures to protect their data, a necessity that adds another layer of complexity and cost to IT implementation.
- Data Breaches: As logistics companies rely more on IT, they become increasingly vulnerable to cyber attacks. These attacks can lead to sensitive information being stolen, including customer data and corporate secrets.
- Operational Disruption: A successful cyber attack can cripple a logistics operation. For instance, ransomware attacks can lock out companies from their own systems, halting operations and causing significant financial damage.
Dependency on Technology
An over-reliance on IT can make logistics operations vulnerable to technological failures. This dependency means that any system downtime or malfunction can have immediate and widespread effects on the entire supply chain, highlighting the need for robust backup plans and manual intervention strategies.
- System Failures: Over-reliance on IT systems means that a single technical glitch can have far-reaching consequences. System outages or failures can disrupt supply chain operations, leading to delays and potentially damaging a company’s reputation.
- Loss of Human Oversight: While automation and IT systems can enhance efficiency, they can also lead to a reduction in human oversight. This can be problematic in situations where human judgement and experience are crucial.
Skill Gap
The integration of advanced IT systems in logistics requires a workforce skilled in these technologies. This presents a challenge in terms of training existing employees and recruiting new talent. The skills gap can be a major hindrance to the effective adoption and utilization of IT in logistics operations.
- Training Needs: The adoption of advanced IT solutions requires employees who are proficient in these technologies. This often necessitates significant investment in training and development, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Recruitment Challenges: There is often a shortage of skilled IT professionals in the logistics sector. Attracting and retaining talent can be challenging, especially in a competitive job market.
Resistance to Change
Incorporating IT into traditional logistics processes often meets with resistance within the organization. This resistance can stem from a reluctance to adapt to new ways of working and a preference for established, familiar routines. Overcoming this resistance is crucial for the successful implementation of IT systems.
- Organizational Challenges: Implementing IT solutions often requires changes in existing processes and workflows. This can meet with resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional ways of working.
- Cultural Shift: Adopting new technologies requires a shift in company culture. Encouraging employees to embrace new systems and abandon old practices can be a difficult and slow process.
Scalability Issues
The scalability of IT systems is a crucial consideration in logistics. As a business grows, its IT infrastructure must be able to accommodate this growth. Failure to do so can lead to inefficiencies and operational bottlenecks, negating some of the key benefits of IT integration.
Adapting to Growth: As a logistics company grows, its IT systems need to scale accordingly. Scaling up IT infrastructure can be complex and expensive, especially if the original systems were not designed with scalability in mind.
Legal and Compliance Issues
The use of IT in logistics is not just a technical challenge but also a legal one. Navigating the complexities of data protection laws and other regulatory requirements is essential. This is especially pertinent for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions, where compliance becomes even more complicated.
- Regulatory Compliance: The use of IT in logistics often involves navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements, especially concerning data protection and privacy laws.
- Global Challenges: For logistics companies operating internationally, complying with various international laws and regulations related to IT can be particularly challenging.
While the advantages of IT in logistics are clear, the disadvantages present significant challenges that need careful consideration and strategic planning to overcome. Businesses must weigh these drawbacks against the benefits to make informed decisions about integrating IT into their logistics operations.
Balancing the Advantages and Disadvantages
To fully reap the advantages of IT in logistics while mitigating the disadvantages of IT in logistics, companies must adopt a strategic approach. This involves careful planning, investing in cybersecurity, providing training to employees, and maintaining a balance between technology and human intervention.
| Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Careful Planning | Ensures effective integration of IT into existing processes. | Requires time and resources for analysis and strategy development. |
| Investing in Cybersecurity | Protects against data breaches and maintains customer trust. | Involves additional costs and continuous updates. |
| Employee Training and Development | Bridges the skill gap and maximizes the use of IT resources. | Requires ongoing investment in training programs. |
| Balancing Technology and Human Intervention | Leverages the efficiency of IT while mitigating dependency risks. | Challenges in maintaining the optimal tech-human balance. |
Final Words
The advantages of IT in logistics significantly outweigh the disadvantages. However, companies must be mindful of the challenges and approach them strategically. With the right balance, IT can continue to revolutionize the logistics sector, making it more efficient, reliable, and customer-focused.
For personalized solutions and expert insights in leveraging IT for your logistics needs, connect with Aeologic Technologies your partner in navigating the digital logistics landscape.