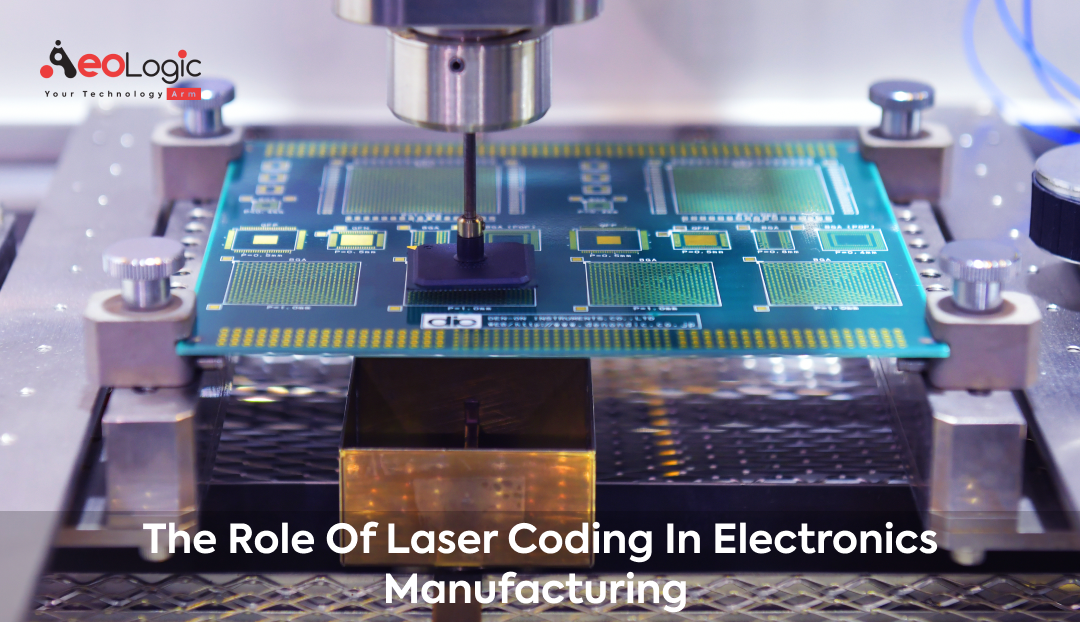
Laser coding is revolutionizing the world of electronics manufacturing. This advanced technology offers unparalleled precision and efficiency, making it a vital tool in the production of electronic components. For those in the industry, understanding and leveraging laser coding is becoming increasingly important. As we delve into the world of laser coding, you’ll discover the pivotal role of laser coding in electronics manufacturing.
What is Laser Coding?
Laser coding, a cutting-edge technology in the field of electronics manufacturing, stands out for its precision and adaptability. At its core, laser coding involves using concentrated light beams to mark or engrave electronic components. This process not only ensures high readability but also maintains the integrity of the parts, which is crucial in the delicate world of electronics.
There are various types of lasers used in coding, each suited for different materials and applications. For instance, fiber lasers are commonly used for metals and plastics due to their fine precision, while CO2 lasers are preferred for coding on glass or organic materials. The choice of laser depends on the material’s properties and the required durability of the coding.
In electronics manufacturing, the ability to apply detailed information on tiny components is essential. Laser coding meets this need by allowing manufacturers to include serial numbers, barcodes, and even intricate graphics on minuscule surfaces. This level of detail is not just about identification; it plays a crucial role in traceability, quality control, and meeting regulatory requirements.
Also Read: Advantages of Laser Barcoding Over Traditional Methods
Top Benefits of Laser Coding in Electronics Manufacturing
The integration of laser coding in electronics manufacturing offers several notable benefits, which are crucial in an industry that constantly strives for precision, efficiency, and traceability.
1. High Precision and Quality: Electronics components are often small and require extremely precise markings for identification and traceability. Laser coding offers superior accuracy compared to traditional methods like inkjet printing. The laser can produce fine, detailed markings that are easily readable, essential for quality control and later servicing or recalls.
2. Durability: Markings made by lasers are permanent and highly resistant to fading, abrasion, and heat, which is critical in electronics that may undergo various stressors during use. This permanence ensures that important information remains legible throughout the product’s life cycle.
3. Non-Contact Process: Laser coding is a non-contact method, meaning the laser does not physically touch the part being marked. This is particularly beneficial in electronics manufacturing where components can be extremely delicate and sensitive to physical stress.
4. Versatility: Lasers can mark a wide range of materials commonly used in electronics manufacturing, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and glass. This flexibility allows for the integration of laser coding across different stages and components of the manufacturing process.
5. Speed and Efficiency: Laser coding is a fast process, enabling high-speed production lines to maintain their pace without compromising on the quality of the markings. This efficiency is vital in meeting the demands of large-scale electronics production.
6. Minimal Maintenance and Operating Costs: Unlike ink-based systems that require regular refilling and maintenance, laser coders have fewer consumables and typically lower maintenance requirements. This results in reduced downtime and long-term cost savings for manufacturers.
7. Environmental Benefits: Laser coding is a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional ink-based coding systems. It eliminates the need for inks, solvents, and other consumables, reducing the environmental impact associated with the disposal of these materials.
8. Improved Traceability and Compliance: In an industry subject to stringent regulations, laser coding ensures that products are easily traceable throughout their lifecycle. This traceability is crucial for compliance with international standards and regulations, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment).
9. Counterfeit Prevention: The high resolution and precision of laser coding make it an effective tool in combatting counterfeit electronics. Unique, hard-to-replicate markings can be etched onto components, enhancing security and brand protection.
10. Integration with Automated Systems: Laser coding systems can be easily integrated with existing automated manufacturing lines and are compatible with Industry 4.0 technologies. This integration allows for seamless operation and greater control over the manufacturing process.
Future Trends in Laser Coding in Electronics
As technology continues to advance, the application of laser coding in electronics manufacturing is poised to evolve further. The future of laser coding for electronics is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends, reflecting the ongoing innovations in laser technology, materials science, and the increasing demands of the electronics industry.
1. Advancements in Laser Technology: Future developments in laser sources, such as improved beam quality, higher power outputs, and greater efficiency, will enhance the capabilities of laser coding systems. This could lead to faster marking speeds, the ability to mark on even more diverse materials, and finer precision, which is critical for increasingly miniaturized electronic components.
2. Integration with Smart Manufacturing: As the trend towards Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing continues, laser coding systems will become more interconnected with other manufacturing processes. Enhanced integration with IoT (Internet of Things) devices and real-time data analysis will facilitate more efficient production lines, predictive maintenance, and adaptive marking processes based on immediate feedback and quality control data.
3. Customization and Personalization: The demand for customized and personalized electronics is growing. Laser coding technology could be adapted to not just mark serial numbers, but also to offer personalized engravings and designs on consumer electronics, adding value and uniqueness to products.
4. Improved Traceability and Security Features: With the growing concern over counterfeit electronics, future laser coding systems may incorporate more advanced security features, such as microprinting or invisible markings only visible under certain conditions. This will enhance traceability and provide a robust method for authenticity verification.
5. Green Laser Coding Technologies: As environmental concerns continue to gain prominence, there will be a push towards developing greener laser coding technologies. This could include more energy-efficient lasers, and the development of processes that have minimal impact on the environment, adhering to increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
6. Ultra-Fast and Ultra-Precise Lasers: The development of ultra-fast and ultra-precise lasers could revolutionize the way delicate electronics are marked. These lasers will be able to code at exceptionally high speeds without generating heat, thus reducing the risk of damaging sensitive electronic components.
7. Software Advancements: Improvements in software that control laser coding systems will enable more complex and precise coding capabilities. This includes advancements in user interfaces, pattern recognition, and automated adjustments for different materials and shapes, allowing for greater flexibility and accuracy in the coding process.
8. Hybrid Systems: We may see the rise of hybrid systems that combine laser coding with other technologies, such as inkjet or 3D printing, to offer versatile solutions that can be adapted to a wide range of materials and requirements in electronics manufacturing.
For you? How Is Barcode Technology Used in Stock Control?
Final Word
Laser coding in electronics manufacturing presents a multitude of benefits ranging from enhanced precision and durability of markings to environmental advantages. Its ability to keep pace with high-speed production processes while ensuring compliance with industry standards makes it an indispensable tool in the modern electronics manufacturing landscape. As the industry continues to evolve, the adoption of laser coding is likely to become more widespread, driven by its numerous advantages and the growing demand for high-quality, traceable, and secure electronic components.
To explore the potential of laser coding and other cutting-edge technologies in electronics manufacturing, consider connecting with Aeologic Technologies.