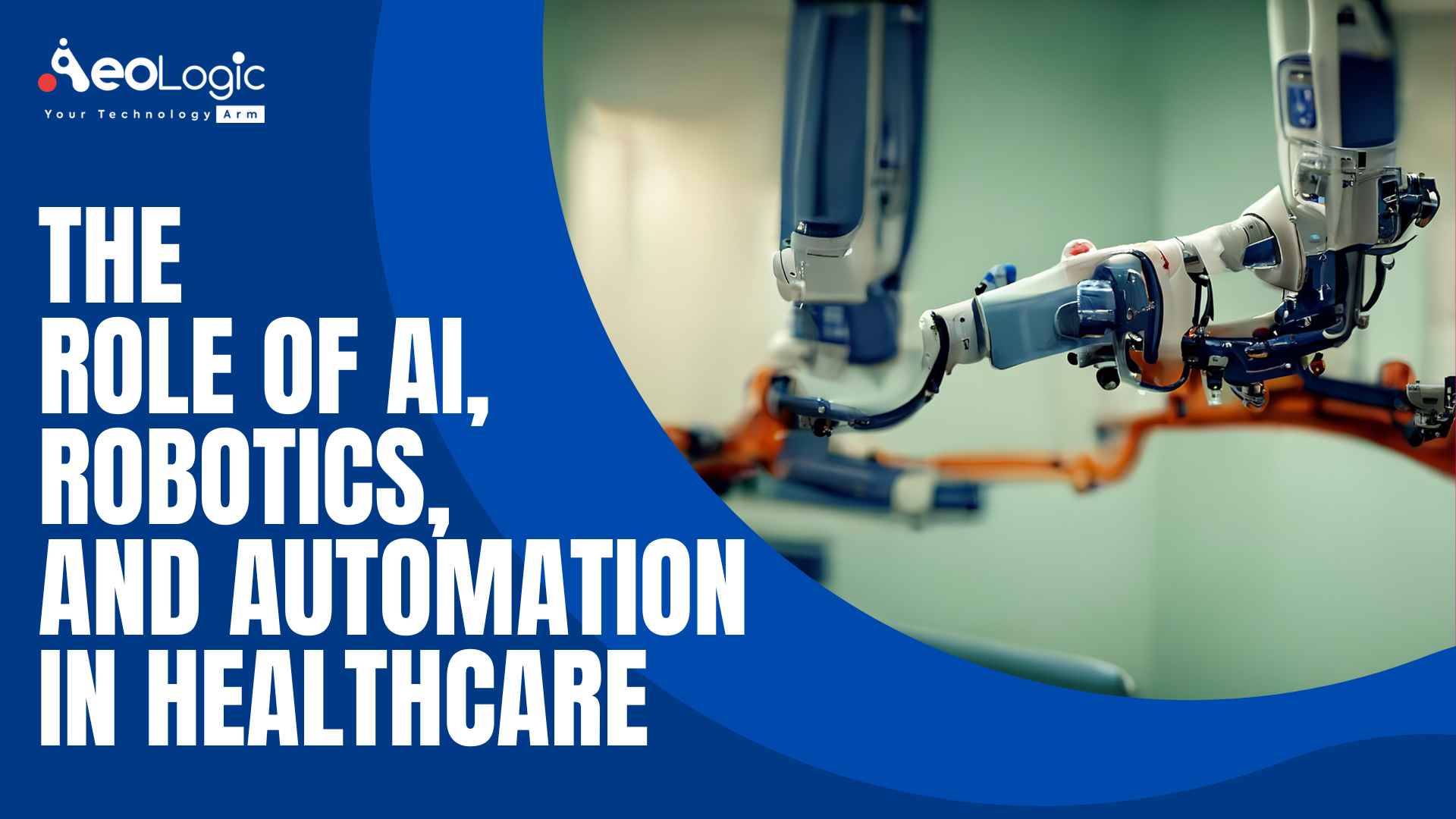
The role of robotics AI and automation in healthcare is getting increasingly sophisticated at doing what humans do. However, more efficient, quicker, and at a lower cost. The role of robotics, AI, and automation in healthcare is vast. Just like in our everyday lives, AI and robotics are hugely a part of our healthcare ecosystem.
Role of Robotics AI and Automation in Healthcare
We have highlighted a few ways that are showcasing how this transformation is currently underway
Treatment
Beyond scanning health data for helping providers in identifying chronically ill individuals who may be at risk of an adverse episode. However, AI will be facilitating clinicians to take a more comprehensive approach to disease management, and better coordinate care plans. As well as helping patients to better manage and comply with their long-term treatment programs.
Healthcare has been using robots for more than 30 years. They are ranging from simple laboratory robots to highly complex surgical robots that can either help a human surgeon or execute operations by themselves. In addition to surgery, they’re used in labs and hospitals for repetitive tasks, in rehabilitation, and physical therapy. As well as in support of those with long-term conditions.
Also read: Information Technology Solutions for Healthcare
Training
The role of robotics AI and automation in healthcare is allowing those in training to go through naturalistic simulations in a way that simple computer-driven algorithms cannot. The initiation of natural speech and the potential of AI computers to draw instantly on a large database of scenarios. This is implying the response to questions, decisions or advice from a trainee can challenge in a way that a human cannot. And the training programme can learn from previous responses from the trainee. Therefore, implying that the challenges can be continually adjusted to meet their learning needs.
Boost your business performance with our automation solutions!
Furthermore, training can be done anywhere; with the power of AI embedded in a smartphone, quick catch-up sessions, after a tricky case in a clinic or while traveling, will be possible.
Diagnosis
IBM’s Watson for Health is facilitating healthcare organizations to apply cognitive technology to unlock vast amounts of health data and power diagnosis. Watson can review and keep far more medical information – every medical journal, symptom, and case study of treatment and response around the globe – exponentially faster than any human.
Also, Google’s DeepMind Health is working in partnership with clinicians, researchers, and patients to answer real-world healthcare problems. The technology is combining machine learning and systems neuroscience. For building powerful general-purpose learning algorithms into neural networks that copy the human brain.
Decision-Making
Improving care is requiring the alignment of big health data with appropriate and timely decisions, and predictive analytics can support clinical decision-making and actions. As well as prioritizing administrative tasks.
Moreover, using pattern recognition for identifying patients at risk of developing a condition – or seeing it deteriorate due to lifestyle, environmental, genomic, or other factors – is another arena where AI is beginning to take hold in the healthcare industry.
Also read: Technology Accelerating Healthcare Innovation
Early Detection
The role of robotics, AI, and automation in healthcare is already being used to detect diseases, such as cancer, more accurately and in their early stages. According to the American Cancer Society, a high proportion of mammograms give false results. Hence, leading to 1 in 2 healthy women being told they have cancer. Subsequently, utilizing AI is enabling the review and translation of mammograms 30 times faster with 99% accuracy. Therefore, reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies.
Thus, enabling doctors and other caregivers to better monitor and detect potentially life-threatening episodes at earlier, more treatable stages.
Keeping Well
One of AI’s biggest potential advantages is helping people stay healthy. So, they don’t require a doctor, or at least not as often. Also, using AI and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) in consumer health applications is already facilitating people.
Subsequently, technology applications and apps are encouraging healthier behavior in individuals. And also, helping with the proactive management of a healthy lifestyle. It is putting consumers in control of their health and well-being.
Additionally, the role of robotics, AI, and automation in healthcare is increasing the ability of healthcare professionals for better understanding the day-to-day patterns and needs of the people they care for. And with that understanding, they will be providing better feedback, guidance, and support for staying healthy.
Conclusion
Robots are having the potential to revolutionize end-of-life care, helping people to remain independent for longer, and reducing the need for hospitalization and care homes. The role of robotics, AI, and automation combined with the advancements in humanoid design is enabling the technology to go even further and have ‘conversations.’ As well as other social interactions with people for keeping aging minds sharp.
Reach out to us at support@aeologic.com to start a conversation followed by a plan for action!
FAQs
How healthcare is using AI Robotics?
The AI is detecting patterns that are leading the patient toward various health conditions. It helps in determining the patient’s current state by analyzing and studying the healthcare records and data. Tests so far have settled that AI is capable of accurately diagnosing diseases in 87% of the cases.
How healthcare is using AI and machine learning?
Nowadays, machine learning — a subset of artificial intelligence- is playing a major role in many health innovations, including the development of new medical procedures, the handling of patient data and records, and the treatment of chronic diseases.