In today’s global marketplace, the food we consume often travels thousands of miles, passing through multiple hands before it reaches our plates. With such a complex supply chain, ensuring the safety and authenticity of food products is paramount. This is where the significance of traceability in food production comes into play.
Why is Traceability in Food Production Vital?
- Ensuring Food Safety: At its core, traceability in food production is about ensuring that the food we eat is safe. By tracking food from its source to the consumer, producers can quickly identify and address any potential food safety issues.
- Building Consumer Trust: When consumers have confidence that they can trace their food back to its source, it fosters trust. In an era where food recalls are not uncommon, being able to provide consumers with this level of transparency can be a significant differentiator for brands.
- Compliance with Regulations: As food safety standards evolve globally, having robust traceability systems in place can help producers stay compliant and avoid potential fines or penalties.
- Sustainability and Ethical Considerations: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental and ethical implications of their food choices. Traceability allows consumers to make informed decisions about the products they buy.
- Economic Efficiency and Waste Reduction: Traceability systems can lead to more efficient supply chains. By tracking products in real-time, producers can optimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and respond more swiftly to market demands.
Also Read: The Importance of Traceability in Laboratory Tests
A Closer Look at the Numbers
- Foodborne Illnesses: According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 600 million – almost 1 in 10 people in the world – fall ill after eating contaminated food each year. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for robust traceability systems.
- Consumer Trust: A recent survey found that 75% of consumers said they would be more likely to buy a product that provides information about its origin and production. This demonstrates the tangible market advantage of traceability in food production.
- Recalls and Financial Impact: The economic cost of food recalls can be staggering. For instance, a single recall can cost a company upwards of $10 million, not to mention the potential damage to the brand’s reputation.
Challenges in Implementing Traceability in Food Production
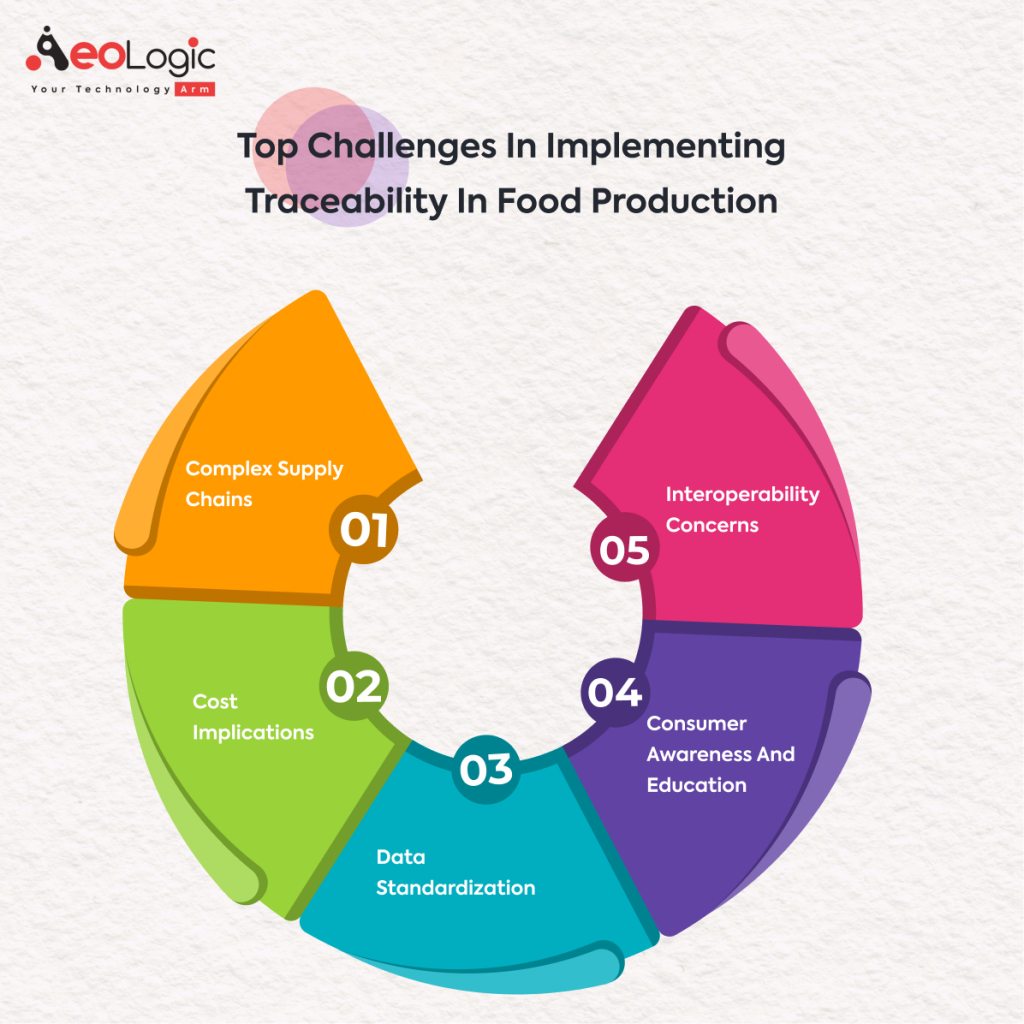
Achieving comprehensive traceability in the vast expanse of global food production is akin to navigating a maze with various intricate turns. The challenges are multifold:
1. Complex Supply Chains
The labyrinthine nature of global food supply chains, with its myriad touchpoints, presents a formidable challenge. Each link in this chain might operate with unique protocols and standards. As ingredients for a single product can originate from numerous countries, this compounds the complexity. This multi-faceted nature demands meticulous planning and execution to ensure accurate traceability.
The journey from farm to table is rarely straightforward.
- Diverse Origins: Ingredients for a single product can originate from numerous countries, each with its own set of regulations and standards.
- Multiple Intermediaries: A single product might pass through numerous hands, from farmers to distributors to retailers.
- Varying Protocols: Different entities in the chain might operate with distinct protocols, leading to inconsistency.
- Logistical Hurdles: Transporting goods across international borders involves dealing with customs, tariffs, and varying shipping regulations.
- Time Sensitivity: Perishable items require swift movement through the supply chain to maintain freshness.
2. Cost Implications
The financial aspects of implementing traceability cannot be underestimated. Initial setup costs can be daunting, especially for smaller players or those operating in regions with economic constraints. Beyond the setup, the recurrent expenses of system maintenance, updates, and potential expansions further strain the financial resources, making it a continuous investment.
Implementing traceability is a valuable endeavor, but it comes with a price tag.
- Initial Setup Costs: High upfront investment is needed to establish a robust traceability system.
- Maintenance: Regular system updates and maintenance can be a recurrent expense.
- Training: Personnel need to be trained to use the system effectively, incurring additional costs.
- Expansion: As the business grows, the traceability system might need to scale, leading to further expenses.
- Unforeseen Challenges: Unexpected challenges, like system breakdowns or data breaches, can result in additional costs.
3. Data Standardization
In the vast arena of food production, there’s a staggering diversity of data formats, stemming from the varied systems used by stakeholders. Bringing coherence to this data chaos, integrating it, and creating a standardized platform is an intensive task. It’s not just about technical integration but also ensuring consistency in data interpretation across the board.
In the digital age, data is king, but managing it can be a royal challenge.
- Diverse Formats: Stakeholders might use different data recording formats, complicating integration.
- Integration Challenges: Merging data from different systems into a cohesive whole is technically challenging.
- Consistency: Ensuring that data is interpreted consistently across the board is crucial.
- Real-time Updates: Data needs to be updated in real-time to reflect the current state of products.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that data remains untampered and authentic is essential.
4. Consumer Awareness and Education
While the modern consumer is becoming more discerning, a sizable segment remains in the dark about the intricacies of traceability. Engaging and educating this segment is essential, but it’s a long-term endeavor, requiring continuous outreach, updates, and engagement strategies.
An informed consumer is a brand’s best ally, but achieving this awareness is an ongoing journey.
- Knowledge Gap: Despite rising awareness, a significant portion of consumers remains uninformed about traceability.
- Outreach Programs: Continuous programs are needed to educate the masses about the importance of traceability.
- Feedback Loop: Engaging consumers and obtaining their feedback can help refine the traceability process.
- Changing Perceptions: Overcoming preconceived notions or misconceptions about traceability can be challenging.
- Adapting to Trends: As consumer behavior evolves, education strategies need to be updated accordingly.
5. Interoperability Concerns
The siloed nature of many traceability systems, designed without a holistic view, can lead to interoperability issues. This means that systems, while effective in isolation, might falter when required to communicate or integrate with others. Addressing these interoperability challenges is crucial to ensure a seamless flow of traceability data across the supply chain.
Technology is a double-edged sword, offering solutions but also presenting compatibility challenges.
- Siloed Systems: Many systems are designed in isolation, leading to compatibility issues.
- Data Flow: Ensuring smooth data flow between different systems is a technical challenge.
- Standardizing Platforms: Creating a standardized platform where all systems can communicate is essential.
- Version Control: Different versions of software might not communicate seamlessly.
- Continuous Updates: As technology evolves, ensuring that all systems remain interoperable requires constant updates.
By diving deep into these challenges, we can appreciate the intricacies involved in establishing traceability in food production. It’s a task that demands a multi-pronged approach, combining technical prowess with strategic foresight.
Also Read our trending blog: Traceability Solutions for Supply Chains with Examples
Technological Innovations Enhancing Traceability Solutions
As the challenges of implementing traceability become increasingly apparent, the silver lining lies in the realm of technology. Cutting-edge technological innovations are paving the way, offering groundbreaking solutions that address the complexities of food traceability head-on.
Blockchain Technology
The rise of blockchain technology has transformed various industries, and food production is no exception. With its decentralized and immutable nature, every transaction recorded on the blockchain provides an unalterable history. This means that all parties involved can trust the data, reducing the chance of fraud or misinformation. Its application in food traceability ensures that every step, from farm to fork, is transparent and verifiable.
IoT and Sensors
As the world becomes more interconnected, the Internet of Things (IoT) offers a myriad of possibilities for food traceability. Sensors attached to food shipments can monitor conditions 24/7, ensuring that perishables like fruits, vegetables, or meats are stored appropriately. With the ability to provide instant notifications in case of deviations, these sensors can prevent spoilage, ensuring the delivery of fresh produce to consumers.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence have revolutionized data analysis. By sifting through vast amounts of data, these technologies can predict future trends, optimize inventory management, and even detect anomalies that could indicate potential issues in the supply chain. Their adaptability means they can learn and improve over time, making the traceability process more efficient and accurate with each iteration.
Cloud Computing
The power of cloud computing lies in its ability to centralize and democratize data access. In the context of food traceability, this means that stakeholders from farmers to retailers can access and update the same data set. This real-time sharing of information ensures that any issues can be quickly identified and addressed, minimizing disruptions and enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
These immersive technologies have extended their reach beyond entertainment. In the realm of food traceability, AR and VR can offer interactive training modules for workers, ensuring they understand the importance and mechanisms of traceability. For consumers, they provide a virtual journey, allowing them to “visit” farms or processing plants, giving them a firsthand look at where their food comes from and how it’s processed, further emphasizing the importance of traceability.
With these technological innovations at the forefront, the food production industry is poised to achieve new heights in traceability, ensuring safety and building a foundation of trust with consumers.
Do you know? Role of Traceability in Sustainable Supply Chain Management
Final Thoughts
Traceability in food production is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity. As the global food supply chain becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of traceability becomes even more pronounced. Whether it’s ensuring food safety, building consumer trust, or staying compliant with regulations, traceability is at the heart of a sustainable and responsible food production system. As consumers, it’s vital to support and demand greater transparency in how our food is produced and sourced.
Interested in taking your food production’s traceability to the next level? Partner with Aeologic Technologies, where innovation meets expertise, to ensure a seamless and efficient traceability process.






