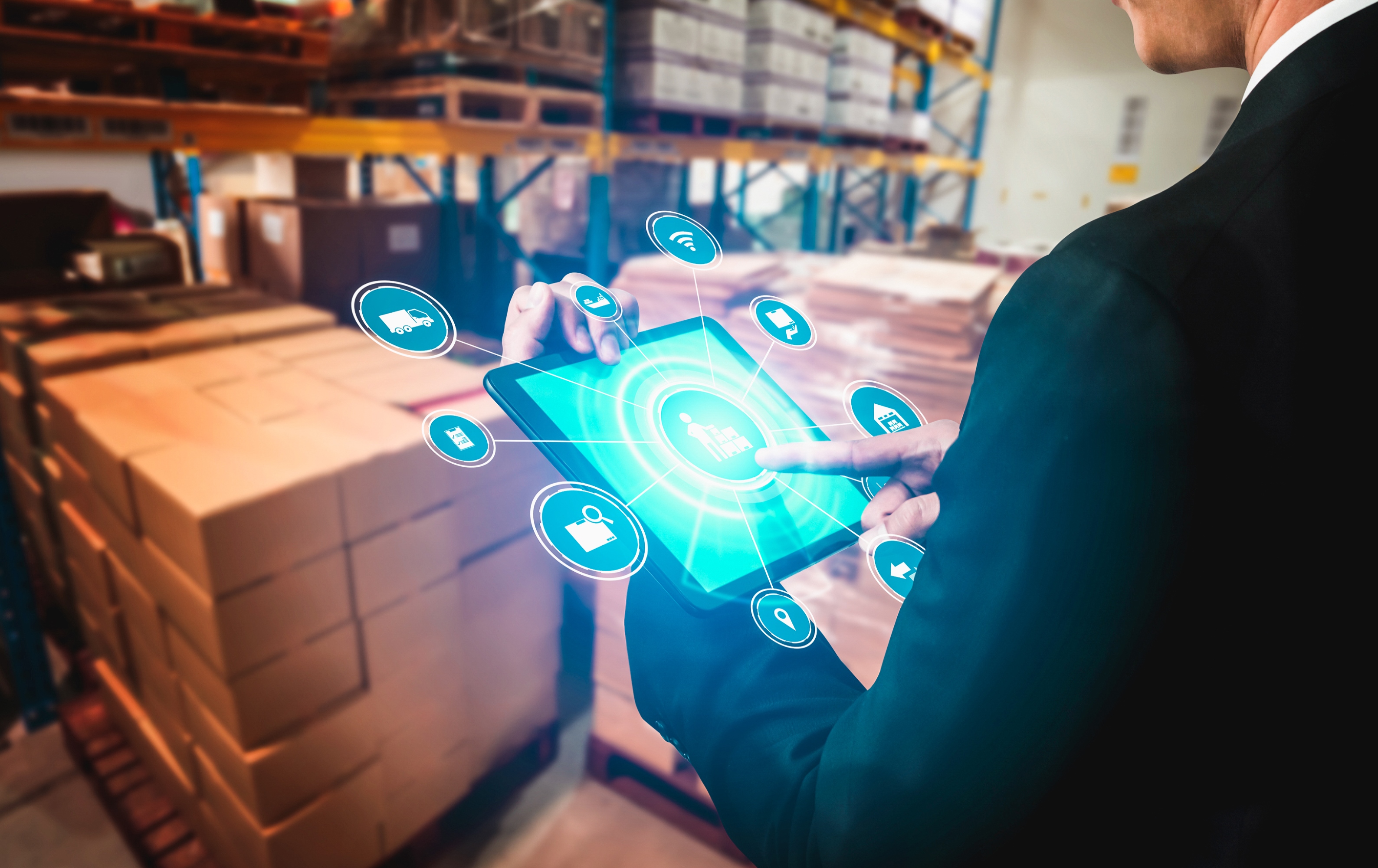
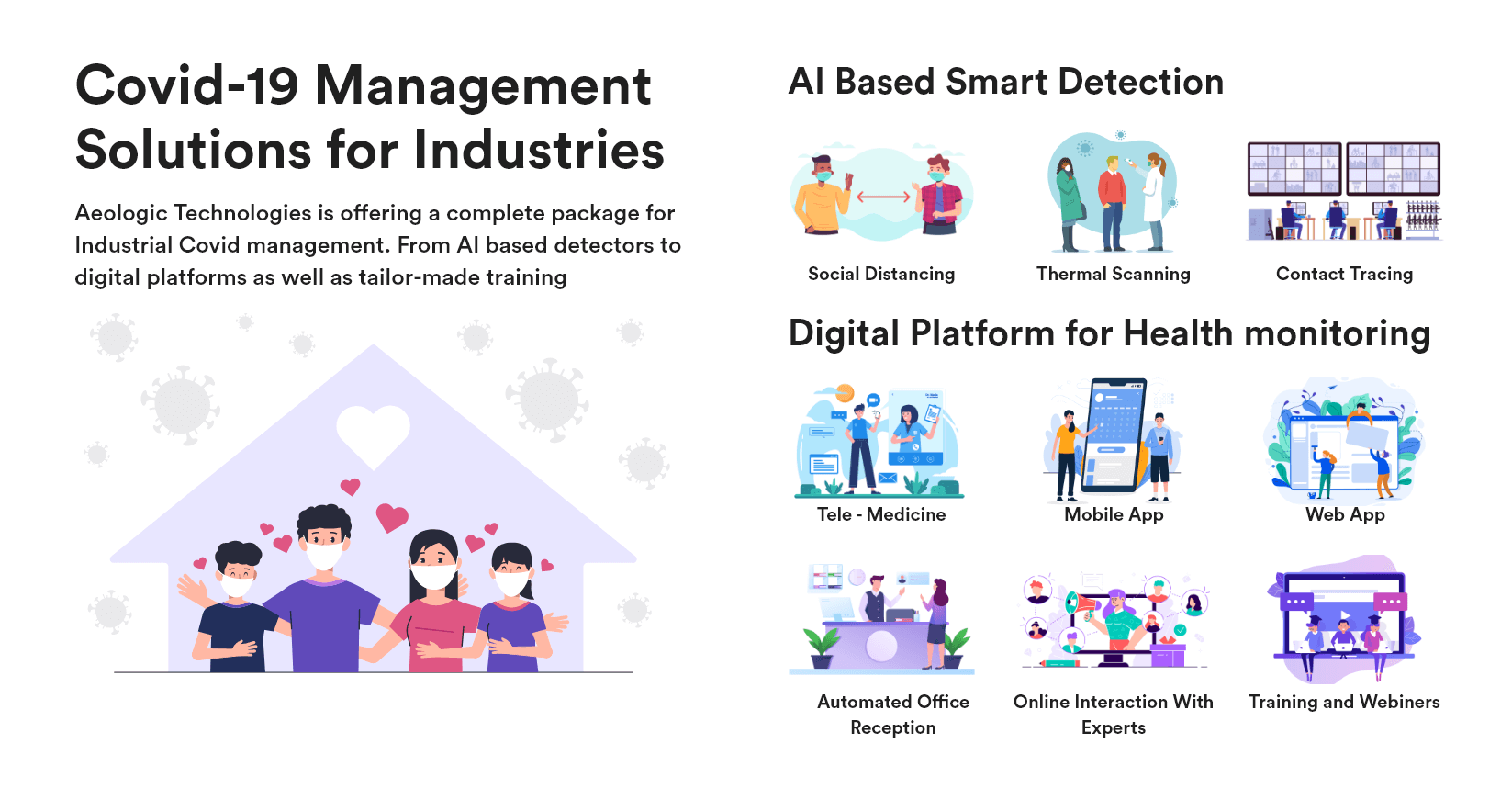
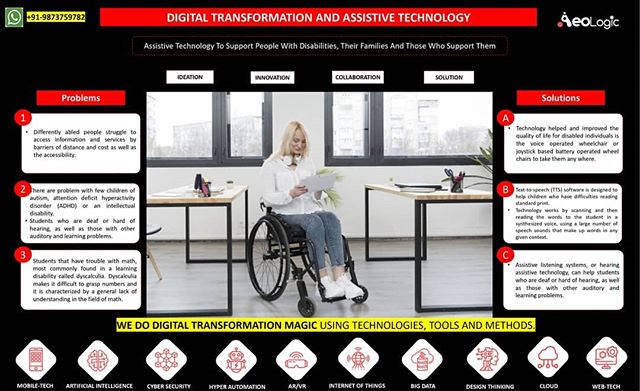
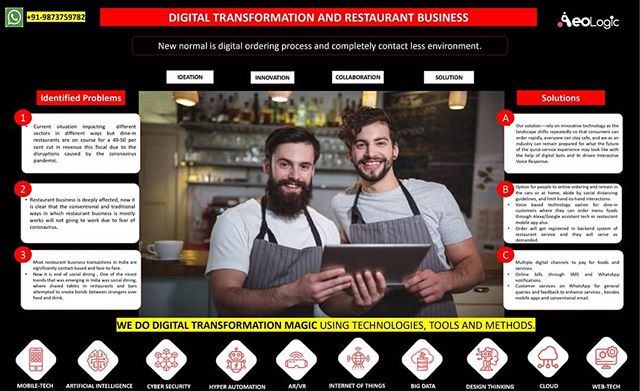
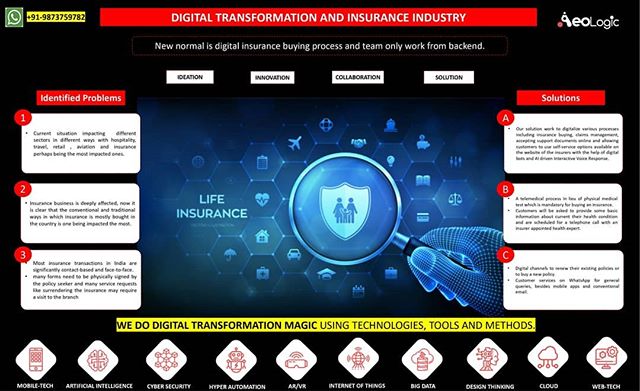
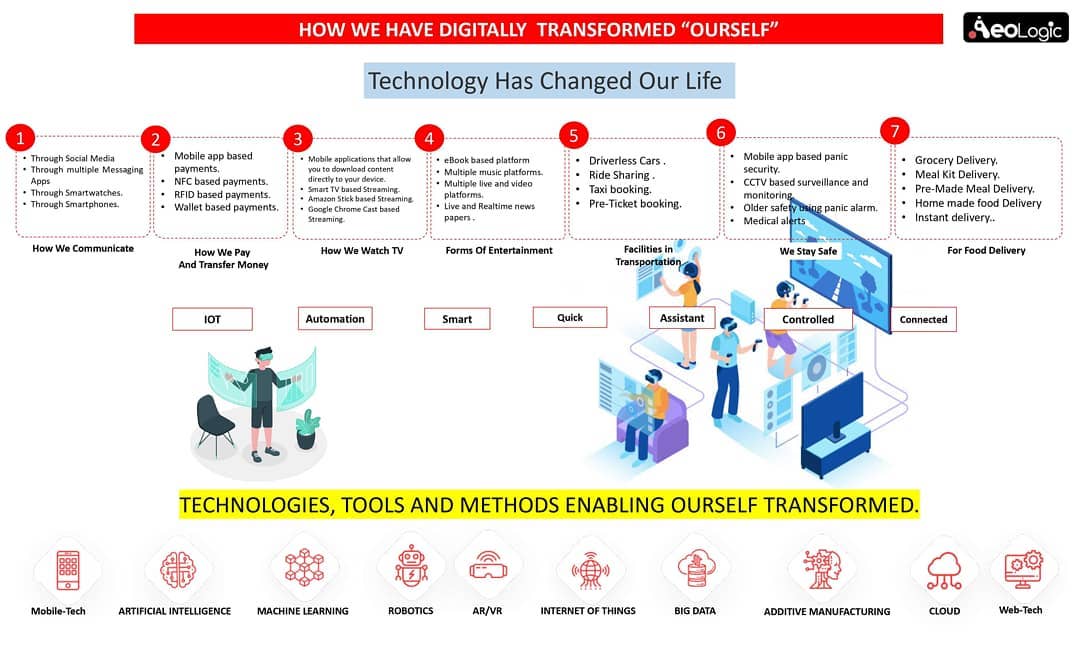
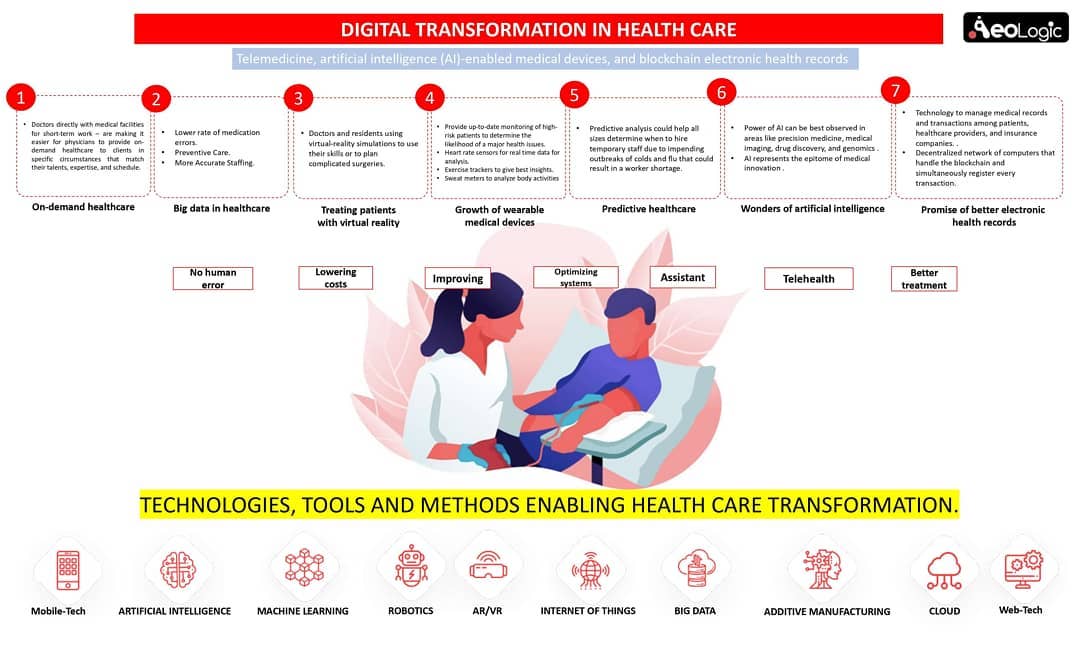
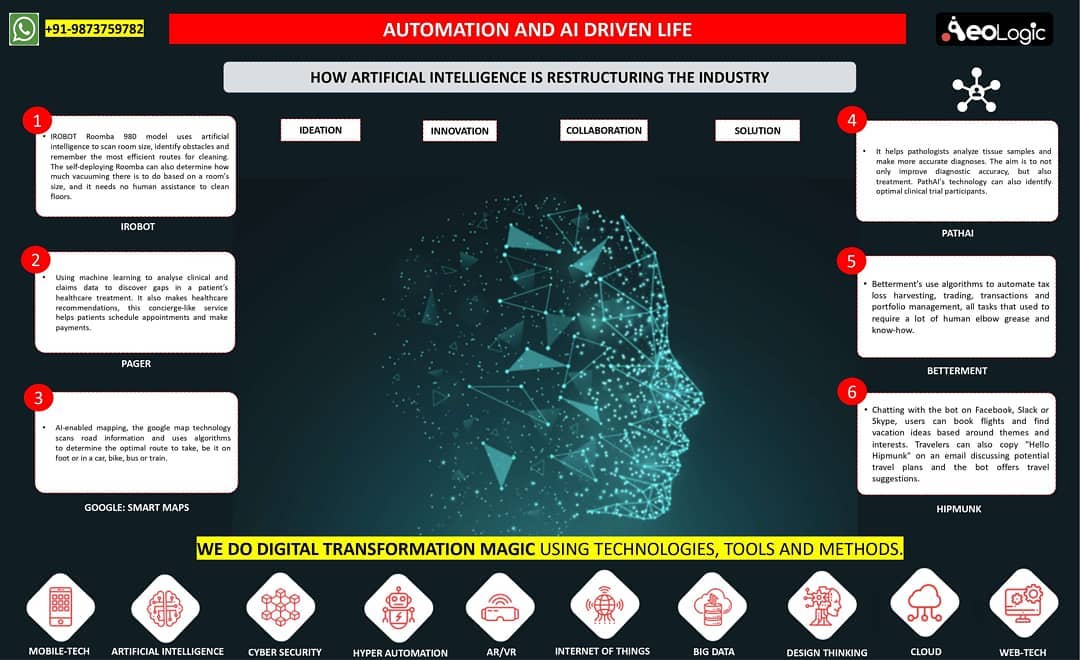
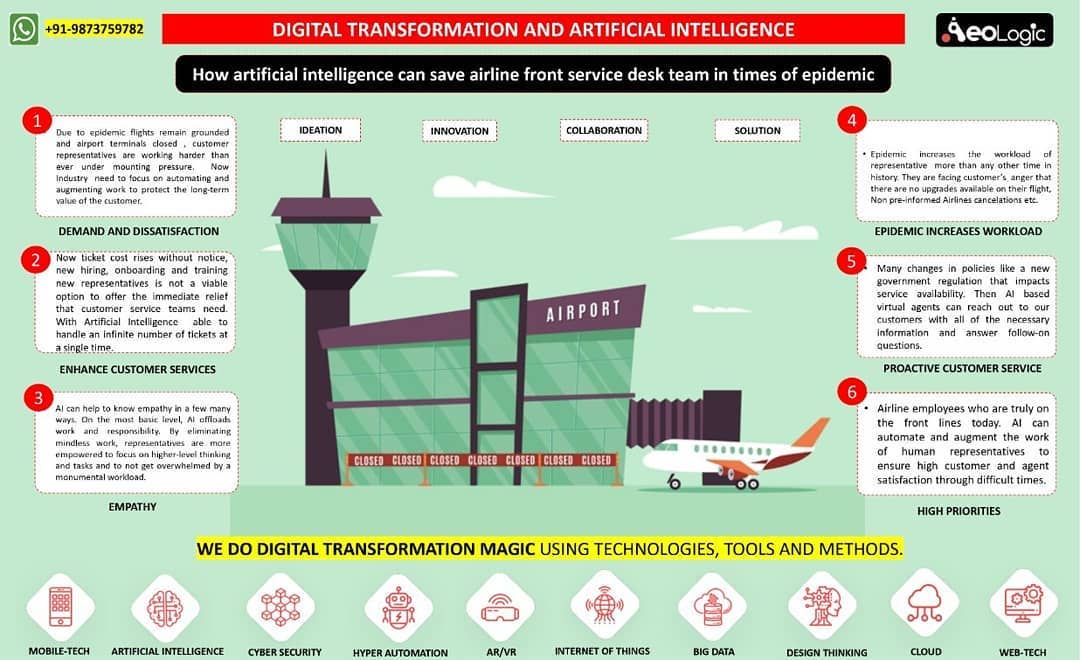
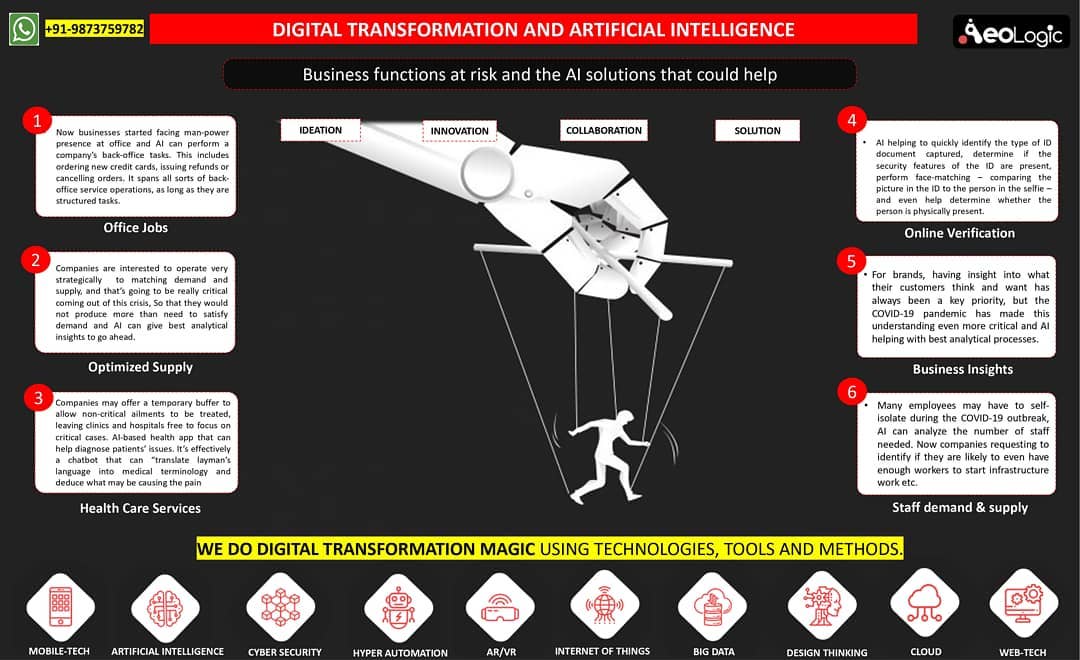
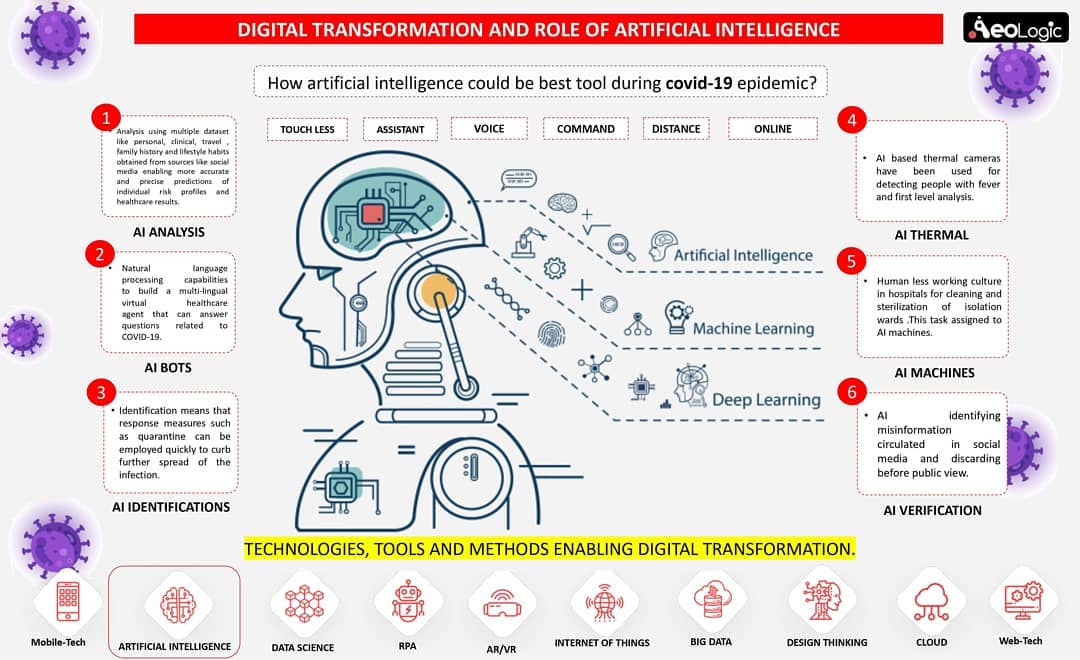
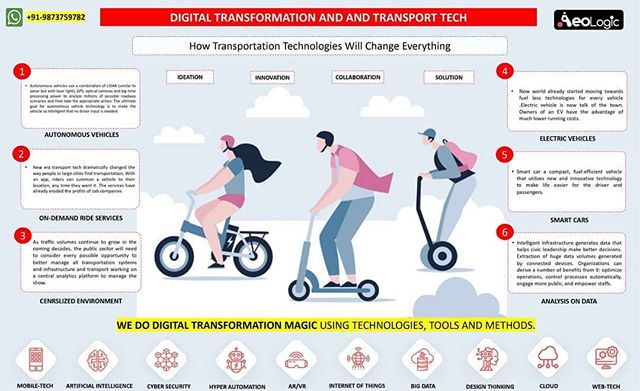
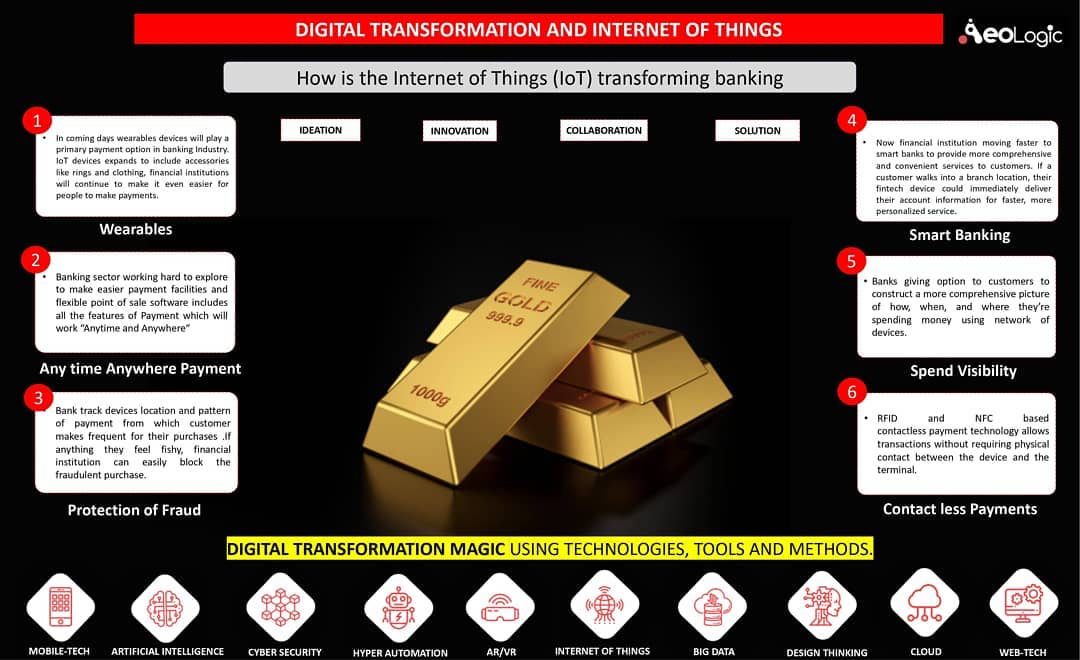
Cold storage automation solution monitors temperature, humidity and various gases like LPG, CO, and Methane, whereas also provide the location coordinates of the warehouse in real time to keep food, vegetables, medicines, and vaccines safe in addition to reduce wastage.
- Easy Installation : IoT sensors are wireless; no costly cabling is required. Sensors magnetically attach to metal posts. No complex mounting required.
- Real-time monitoring : The cloud-based solution is easily accessible anywhere with an internet connection.
- Real-time notifications : Notifications of temperature changes are immediate with on screen pop ups, emails and SMS notifications.
- Compliance Reports : Produce compliance reports with up to a year of data.